Economy
Expansion of India’s Digital Rupee (CBDC):
-
- Context: The Reserve Bank of India announced the expansion of the Digital Rupee (Central Bank Digital Currency, CBDC) pilot across additional cities, covering millions of users and merchants. This reflects India’s strategic push in digital money and financial innovation.
- RBI’s Digital Rupee (e₹) is India’s sovereign digital currency, a digital form of the rupee issued by RBI.
- The pilot has been expanded to cover more cities and users, with millions already onboarded under the retail CBDC pilot.
- Over 5 million users and 500,000 merchants are reported onboarded, indicating rapid adoption.
- Expansion improves penetration of digital currency use cases for payments and settlements.
- A digital rupee runs through an e-wallet provided by banks or fintech firms and can be used like physical cash for payments.
- Digital rupee is legal tender and a liability of the RBI, authorized under the RBI Act.
- It is being tried in both retail and wholesale CBDC segments for broader ecosystem testing.
- CBDC is interoperable with UPI QR codes, led by earlier RBI strategy to integrate payment systems.
- Offline transaction capabilities are under pilot testing to enable digital payments without constant connectivity.
- India is among the few countries globally piloting CBDC at scale.

(RBI)
Union Budget 2026-27 (Priority Sectors & Fiscal Roadmap):
-
- Context: The Union Budget 2026-27 was presented in Parliament on 1 February 2026 by Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman, outlining the Government’s fiscal plans and policy priorities for the year.
-
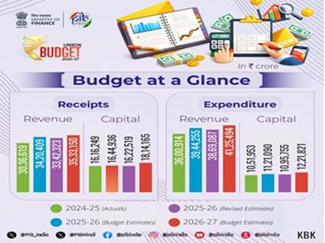
- Total Government expenditure estimated at ₹53.5 lakh crore; non-debt receipts at ₹36.5 lakh crore.
- Net market borrowings pegged at ₹11.7 lakh crore to finance the fiscal deficit.
- Fiscal deficit targeted at 4.3 % of GDP for FY 2026-27.
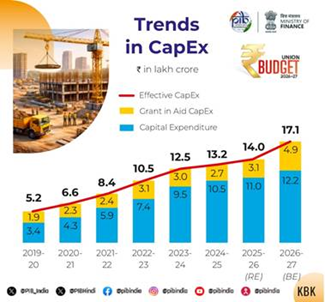
- Capital expenditure was set at ₹12.2 lakh crore, emphasizing infrastructure-led growth.
-
- A new Income Tax Act, 2025 to be implemented from April 2026 to simplify tax compliance and reduce litigation.
- Tax holiday until 2047 for foreign companies providing cloud/AI services from India.
- Customs and excise reforms proposed for ease of living and to support domestic value addition.
- Special measures to support MSMEs, exporters and start-ups through duty rationalization.
- Focus on fiscal consolidation while boosting growth and investment.
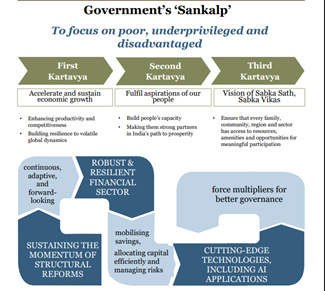
- Emphasis on “3 Kartavyas” – sustaining growth, people-centric reforms, and inclusive development.

(PIB)
India-US Trade Deal:
-
- Context: India-US trade deal, sharply cut U.S. tariffs on Indian goods from 50 % to 18 %, significantly boosting Indian markets and export prospects.
- The deal is expected to reduce trade tensions and enhance bilateral economic cooperation.
- Indian stock markets rallied sharply after the announcement; Sensex and Nifty gained significantly.
- Textile and export-linked sectors saw upper-circuit gains due to improved market access prospects.
- Easing tariffs may enhance competitiveness of Indian exports against rivals like Vietnam, Malaysia, Bangladesh, etc.
- The deal may attract foreign institutional investors back into Indian markets due to sentiment improvement.
- Reduced tariff barriers could shift global supply chains and enhance India’s export basket.
(IE)
The 16th finance commission (key recommendations & fiscal federalism):
-
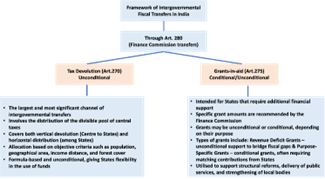
- Context: The 16th Finance Commission recommended retaining states’ share in central taxes at 41 %.
- It acknowledged tight fiscal spaces for states under the GST revenue regime.
- Horizontal devolution formulas were revised to enhance weightage to contribution to GDP.
- States are rewarded for productive governance outcomes rather than just tax effort.
- Slow reforms in certain states could otherwise hamper equitable growth.
- Weightage assigned to demographic performance was reduced to avoid penalising growing populations.
- Implementation changes are to be gradual to avoid abrupt fiscal shocks.
- Focus on enhancing performance incentives aligns with cooperative federalism principles.
- The commission’s recommendations impact Centre–state fiscal relations for 2026-31.
(TH)
Rail Expansion in Budget 2026–27:
-
- Context: Union Budget allocated ₹2,911 crore for rail expansion to hill states under the 2026-27 Budget, reflecting focused transport infrastructure support.
- ₹2,911 crore allocated for railway expansion in hill states like Himachal Pradesh.
- Part of broader strategy to improve transport connectivity.
- Enhanced rail links boost tourism and regional mobility.
- Budget reflects prioritisation of inclusive infrastructure planning.
- Railway connectivity improves economic integration of remote regions.
- Funds support terrain-specific engineering challenges.
- Aligns with broader rail capital expenditure push in the budget.
- Strategic rail expansion can support defense logistics in sensitive border regions.
- Boosts last-mile connectivity in hilly belts.
- Complements high-speed rail corridors and freight expansions.

(IE)
Geography, Mapping, Ecology & Environment
India’s Critical Minerals Strategy:
-
- Context: India’s push to secure critical minerals (lithium, cobalt, rare earths) under Budget announcements.
- Critical minerals essential for EVs, semiconductors, renewables.
- India heavily import-dependent, especially on China.
- Budget announced rare-earth corridor development.
- Public-private mining partnerships encouraged.
- Overseas asset acquisition strategy revived.
- Linked to National Electric Mobility Mission.
- Environmental clearances remain a challenge.
- Geological Survey of India tasked with exploration.
- Strategic autonomy is a key objective.
- Aligns with Quad supply-chain resilience agenda.

(PIB)
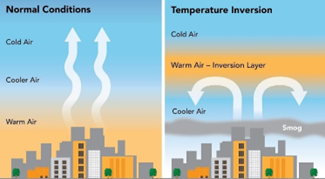
Temperature Inversion & Winter Pollution:
-
- Context: Cold wave and inversion conditions in North India.
- Inversion traps pollutants near surface.
- Common in winter due to calm winds.
- Leads to smog and poor AQI.
- Affects respiratory health.
- Limits vertical mixing of air.
- Fog formation increases.
- Urban heat islands worsen impact.
- Policy relevance for GRAP measures.
- Climate change may increase frequency.
- Impacts aviation and rail operations.
(DTE)
Science & Technology
AI-Driven Governance Platforms – Bharat-VISTAAR:
-
- Context: In the Union Budget 2026-27, the Government of India announced the launch of Bharat-VISTAAR (Virtually Integrated System to Access Agricultural Resources), a flagship AI-driven governance platform designed to revolutionize the agricultural sector.
- Bharat-VISTAAR serves as a Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) that integrates fragmented agricultural resources into a single, intelligent interface.
Key Features and Objectives:
-
- Multilingual AI advisory: The platform uses advanced AI systems to provide real-time, customized advisory services in multiple regional languages, ensuring accessibility for farmers across diverse linguistic regions.
- Integrated data ecosystem: It merges existing agristack digital records with the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) package of practices.
- Decision support: Farmers receive location-specific and crop-specific guidance on:
- Sowing and Irrigation: Optimal timing based on soil health and weather forecasts.
- Input management: Precise recommendations for fertilization and pest control to reduce costs and risks.
- Risk mitigation: Early warnings for weather shocks, pest outbreaks, and market fluctuations.
- Democratizing intelligence: By bridging the gap between scientific research and field application, it aims to enhance farm productivity and empower small-scale farmers with data-driven insights.
- Multilingual AI advisory: The platform uses advanced AI systems to provide real-time, customized advisory services in multiple regional languages, ensuring accessibility for farmers across diverse linguistic regions.
Implementation details:
-
- Allocation: The government has allocated ₹150 crore for the 2026-27 financial year to scale this initiative.
- Reach: Initial launch focuses on Hindi and English, with rapid expansion planned for all major Indian languages.
- Digital integration: The platform integrates with the Kisan Call Center and uses AI bots (developed with technologies like Bhashini) to deliver advice via mobile tools like Telegram.
- Bharat-VISTAAR is part of a broader 2026 AI-driven growth strategy that includes:
- Financial Compliance: Using AI to detect financial trails in GST and income tax.
- Logistics: Embedding AI in customs reforms for efficiency.
- Inclusion: AI-integrated assistive devices for persons with disabilities.
(ET)
Spread the Word
The post Prelims Mantra – (03/02/2026) appeared first on Lukmaan IAS.