Indian Polity
Comptroller and Auditor-General (CAG):
-
- Context: CAG of India has granted in-principle approval for the creation of two new specialised cadres for more centralisation.
- These cadres are within its Indian Audit and Accounts Department, and they will be called the Central Revenue Audit (CRA) Cadre and the Central Expenditure Audit (CEA) Cadre.
- Constitutional body: Established under Article 148 of the Indian Constitution.
- Appointment: Appointed by the President of India.
- Tenure: Holds office for 6 years or up to age 65, whichever is earlier.
- Duties: Audits receipts and expenditure of the Union, States, and government-owned bodies.
- Reports: Submitted to the President or Governor, who lays them before Parliament or State Legislature.
- Independence: Can be removed only in the same manner as a Supreme Court judge.
- Significance: Ensures accountability of public finances and acts as the guardian of the public purse.
(TH)
Two Census mobile applications and test portal for self-enumeration launched:
-
- The Registrar-General and Census Commissioner of India launched two mobile applications this week in preparation for the trial phase of the country’s first digital Census in 2027.
- The two applications available on Google Play Store: Digital Layout Map (DLM) and Census 2027 – Houselist.
- The apps are compatible with both Android and Apple phones and can only be downloaded by authorised personnel.
- A Self-Enumeration facility will be made available through the Census Portal from 1st to 7th November 2025.
- The app will record building coordinates (latitude and longitude for each structure), the names of localities, roads or streets, building numbers (if available; otherwise, temporary Census house numbers will be assigned by enumerators), and building type (pucca or kutcha).
(TH)
International Developments
Abraham Accords:
-
- Context: Kazakhstan to announce it will join Abraham Accords.
- Signed in: 2020 (brokered by the United States).
- Parties involved: Israel, United Arab Emirates (UAE), and Bahrain (later joined by Sudan and Morocco).
- Purpose: To normalize diplomatic relations between Israel and Arab nations.
- Significance: Marked a major shift in West Asian geopolitics, promoting economic, security, and technological cooperation.
- India’s relevance: Opens new avenues for regional connectivity, energy cooperation, and strategic partnerships in West Asia.
(TH)
India Deepens Trade Engagement with Latin America:
-
- Context: 9th Round of India-Peru Trade Agreement and 3rd Round of India-Chile CEPA Negotiations Successfully Concluded.
- India concluded the 9th round of trade‑agreement negotiations with Peru (3‑5 Nov 2025 in Lima) covering goods & services, rules of origin, technical barriers, customs, dispute settlement and critical minerals.
- Simultaneously, the 3rd round of the Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) negotiations with Chile (27‑30 Oct 2025 in Santiago) addressed trade in goods & services, investment, IPR, TBT/SPS and economic cooperation.
- These developments highlight India’s strategic push to deepen economic ties with Latin America, pursuing enhanced market access, supply‑chain resilience and cooperation in critical minerals, textiles, pharmaceuticals, food‑processing and automobiles.
Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA)
-
-
- Definition: A CEPA is a trade agreement between countries covering trade in goods, services, investment, IPR, and economic cooperation, aiming for deeper economic integration.
- Scope: Goes beyond traditional Free Trade Agreements (FTA) by including services, investment, intellectual property, and regulatory cooperation.
- India’s CEPAs: Signed with countries like South Korea, Japan, UAE, and Chile; negotiations ongoing with several Latin American nations.
- Objectives: Promote market access, trade diversification, investment flows, and supply chain resilience.
- Significance for India: Enhances exports, bilateral investment, technological collaboration, and strengthens strategic economic partnerships.
- Both negotiations envisaged time‑bound conclusion and set next steps: inter‑sessional meetings ahead of the next Peru round in New Delhi in January 2026.
-
(TH)
Geography, Mapping, Ecology & Environment
Typhoon Kalmaegi:
-
- Context: Philippines death toll tops 140 as typhoon heads towards Vietnam.
- Region affected: Western North Pacific; mainly the Philippines, China, and Vietnam.
- Formation: Originated over the western Pacific Ocean, typically forming during September.
- Category: Classified as a Category 3 typhoon on the Saffir–Simpson scale during its peak.
- Impact: Caused heavy rainfall, flooding, and strong winds, leading to large-scale agricultural and infrastructural damage.
- Naming: The name Kalmaegi was contributed by Macau, meaning seagull in Cantonese.
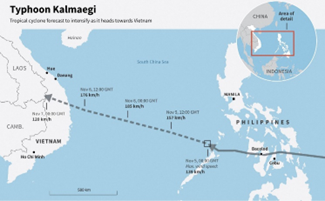
(TH)
History, Art & Culture
150 Years of Vande Mataram:
-
- Context: For its 150th anniversary (2025), the Government of India has planned nationwide and global commemorations, including special events, a commemorative stamp & coin, cultural programmes, exhibitions, and media outreach.

-
- Composed by Bankim Chandra Chatterjee, first published on 7 November 1875, later included in his novel Anandamath (1882).

-
- Adopted as India’s National Song by the Constituent Assembly of India in 1950, given equal honour with the national anthem.
- Played a prominent role in India’s freedom movement: used as a slogan from August 1905, featured in Swadeshi protests, and became a unifying cry across regions.

(TH)
PRACTICE MCQ’S
Q1. With reference to Typhoon Kalmaegi, consider the following statements:
1. Typhoon Kalmaegi originated in the Western Pacific Ocean and primarily affected the Philippines and parts of East Asia.
2. The name ‘Kalmaegi’ was given by Japan and refers to a type of tropical bird found in the Pacific region.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: A
Explanation: The name Kalmaegi was contributed by Macau, meaning seagull in Cantonese, not by Japan.
Q2. With reference to tropical typhoons, consider the following statements:
1. Typhoons are tropical cyclones that form over the South Atlantic Ocean.
2. In the Indian Ocean region, such systems are known as hurricanes.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 only
b) 2 only
c) Both 1 and 2
d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer: D
Explanation: Typhoons form over the western North Pacific Ocean, and in the Indian Ocean, they are called cyclones, not hurricanes.
Q3. With reference to the Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG) of India, consider the following statements:
1. The CAG is appointed by the President of India and can be removed in the same manner as a High Court judge.
2. The CAG audits the accounts of both the Union and State governments.
3. The reports of the CAG are submitted directly to Parliament without the involvement of the President.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 only
c) 2 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
Explanation:
-
- The CAG is removed like a Supreme Court judge, not a High Court judge.
- Reports are submitted to the President or Governor, who then lays them before Parliament or the State Legislature.
Q4. With reference to Vande Mataram, consider the following statements:
a) It was composed by Rabindranath Tagore in 1905 during the Swadeshi Movement.
b) It was first published in the novel Gitanjali in 1875.
c) It was adopted as India’s National Song by the Constituent Assembly in 1950.
d) It was originally written in Urdu and later translated into Bengali.
Answer: C
Explanation:
Vande Mataram was composed by Bankim Chandra Chatterjee and first published in 1875, later included in his novel Anandamath (1882).
It became a symbol of India’s freedom movement and was adopted as the National Song by the Constituent Assembly in 1950, receiving equal status and honour with the National Anthem.
Q5. With reference to Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreements (CEPA), consider the following statements:
1. CEPA covers only trade in goods between countries, like a Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
2. CEPA includes trade in services, investment, intellectual property, and regulatory cooperation.
3. India has signed CEPAs with countries like Japan, South Korea, and UAE.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
a) 1 and 2 only
b) 2 and 3 only
c) 1 and 3 only
d) 1, 2 and 3
Answer: B
Explanation: Unlike FTAs, CEPA covers goods, services, investment, IPR, and regulatory cooperation. India has signed CEPAs with Japan, South Korea, UAE, and others.
Spread the Word
The post Prelims Mantra – (07/11/2025) appeared first on Lukmaan IAS.